1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
|
<!--
title: "Update the Netdata Agent"
description: "If you opted out of automatic updates, you need to update your Netdata Agent to the latest nightly or stable version."
custom_edit_url: https://github.com/netdata/netdata/edit/master/packaging/installer/UPDATE.md
-->
# Update the Netdata Agent
By default, the Netdata Agent automatically updates with the latest nightly or stable version depending on which
you installed. If you opted out of automatic updates, you need to update your Netdata Agent to the latest nightly
or stable version. You can also [enable or disable automatic updates on an existing install](#control-automatic-updates).
> 💡 Looking to reinstall the Netdata Agent to enable a feature, update an Agent that cannot update automatically, or
> troubleshoot an error during the installation process? See our [reinstallation doc](/packaging/installer/REINSTALL.md)
> for reinstallation steps.
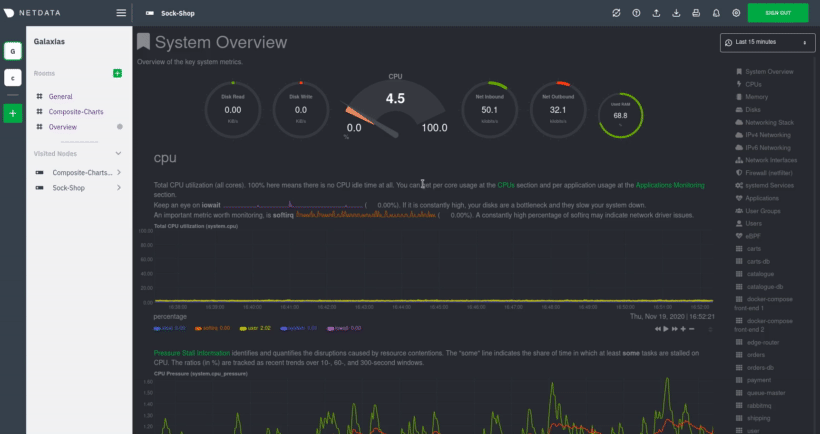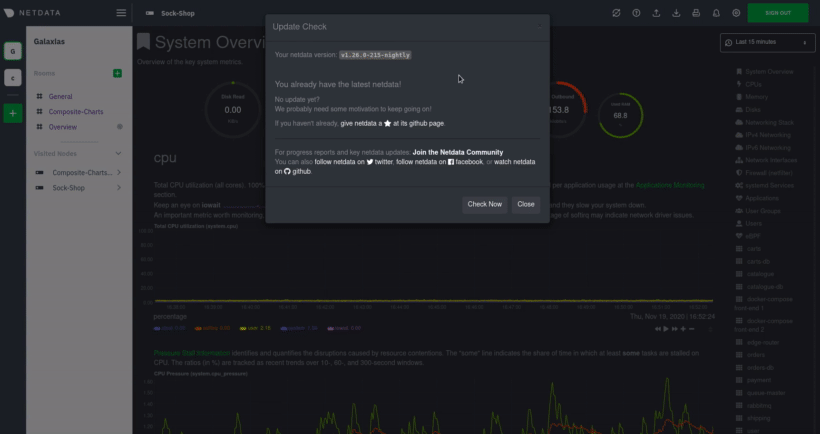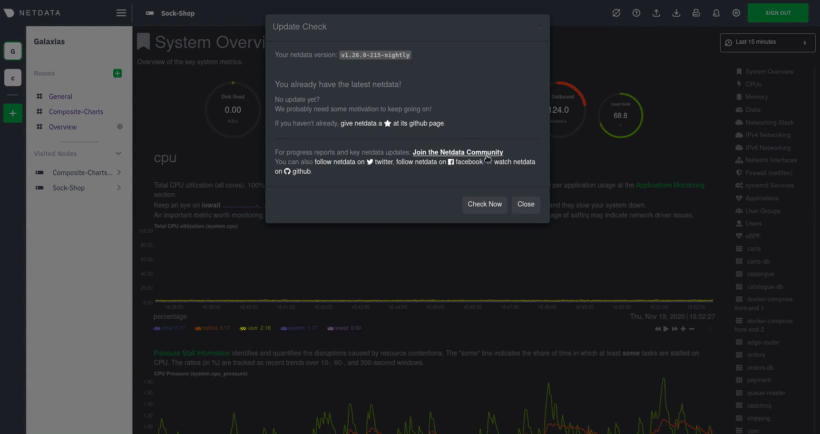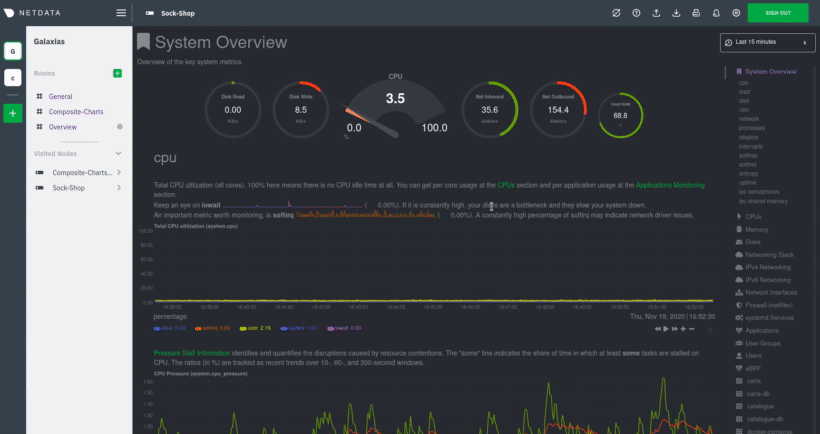
Before you update the Netdata Agent, check to see if your Netdata Agent is already up-to-date by clicking on the update
icon in the local Agent dashboard's top navigation. This modal informs you whether your Agent needs an update or not.
## Determine which installation method you used
Starting with netdata v1.33.0, you can use Netdata itself to determine the installation type by running:
```bash
netdata -W buildinfo | grep 'Install type:'
```
If this produces no output, you have an older install and will have to manually look in the Netdata config directory.
If you are not sure where your Netdata config directory is, see the [configuration doc](/docs/configure/nodes.md). In
most installations, this is `/etc/netdata`.
Use `cd` to navigate to the Netdata config directory, then use `ls -a` to look for a file called `.install-type`.
- If the `.install-type` file doex not exist, look for a file in the same directory called `.environment`.
- If the `.environment` file does not exist, then you have a ‘custom’ install.
- If the `.environment` file does exist, then you have either a ‘static’ or ‘build’ install.
- If the `.install-type` file does exist, check it’s contents with `cat .install-type`.
- The value of the `INSTALL_TYPE` key indicates what type of install you have.
The exact update method to use depends on the install type:
- Installs with an install type of 'custom' usually indicate installing a third-party package through the system
package manager. To update these installs, you should update the package just like you would any other package
on your system.
- Installs with an install type starting with `binpkg` or ending with `build` or `static` can be updated using
our [regular update method](#updates-for-most-systems).
- Installs with an install type of 'oci' were created from our official Docker images, and should be updated
using our [Docker](#docker) update procedure.
- macOS users should check [our update instructions for macOS](#macos).
- Manually built installs should check [our update instructions for manual builds](#manual-installation-from-git).
## Updates for most systems
In most cases, you can update netdata using our one-line installation script. This script will automatically
run the update script that was installed as part of the initial install (even if you disabled automatic updates)
and preserve the existing install options you specified.
If you installed Netdata using an installation prefix, you will need to add an `--install` option specifying
that prefix to this command to make sure it finds Netdata.
```bash
wget -O /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh && sh /tmp/netdata-kickstart.sh
```
> ❗ If the above command fails, you can [reinstall
> Netdata](/packaging/installer/REINSTALL.md#one-line-installer-script-kickstartsh) to get the latest version. This also
> preserves your [configuration](/docs/configure/nodes.md) in `netdata.conf` or other files.
## Docker
Docker-based installations do not update automatically. To update an Netdata Agent running in a Docker container, you
must pull the [latest image from Docker Hub](https://hub.docker.com/r/netdata/netdata), stop and remove the container,
and re-create it using the latest image.
First, pull the latest version of the image.
```bash
docker pull netdata/netdata:latest
```
Next, to stop and remove any containers using the `netdata/netdata` image. Replace `netdata` if you changed it from the
default.
```bash
docker stop netdata
docker rm netdata
```
You can now re-create your Netdata container using the `docker` command or a `docker-compose.yml` file. See our [Docker
installation instructions](/packaging/docker/README.md#create-a-new-netdata-agent-container) for details.
## macOS
If you installed Netdata on your macOS system using Homebrew, you can explicitly request an update:
```bash
brew upgrade netdata
```
Homebrew downloads the latest Netdata via the
[formulae](https://github.com/Homebrew/homebrew-core/blob/master/Formula/netdata.rb), ensures all dependencies are met,
and updates Netdata via reinstallation.
If you instead installed Netdata using our one-line installation script, you can use our [regular update
instructions](#updates-for-most-systems) to update Netdata.
## Manual installation from Git
If you installed [Netdata manually from Git](/packaging/installer/methods/manual.md), you can run that installer again
to update your agent. First, run our automatic requirements installer, which works on many Linux distributions, to
ensure your system has the dependencies necessary for new features.
```bash
bash <(curl -sSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/netdata/netdata/master/packaging/installer/install-required-packages.sh)
```
Navigate to the directory where you first cloned the Netdata repository, pull the latest source code, and run
`netdata-install.sh` again. This process compiles Netdata with the latest source code and updates it via reinstallation.
```bash
cd /path/to/netdata/git
git pull origin master
sudo ./netdata-installer.sh
```
> ⚠️ If you installed Netdata with any optional parameters, such as `--no-updates` to disable automatic updates, and
> want to retain those settings, you need to set them again during this process.
## Control automatic updates
Starting with Netdata v1.34.0, you can easily enable or disable automatic updates on an existing installation
using the updater script.
For most installs on Linux, you can enable auto-updates with:
```bash
/usr/libexec/netdata/netdata-updater.sh --enable-auto-updates
```
and disable them with:
```bash
/usr/libexec/netdata/netdata-updater.sh --disable-auto-updates
```
For static installs, instead use:
```bash
/opt/netdata/usr/libexec/netdata/netdata-updater.sh --enable-auto-updates
```
and:
```bash
/opt/netdata/usr/libexec/netdata/netdata-updater.sh --disable-auto-updates
```
|
