diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'health/tutorials/stop-notifications-alarms.md')
| -rw-r--r-- | health/tutorials/stop-notifications-alarms.md | 85 |
1 files changed, 85 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/health/tutorials/stop-notifications-alarms.md b/health/tutorials/stop-notifications-alarms.md new file mode 100644 index 0000000000..9b24e5dcbd --- /dev/null +++ b/health/tutorials/stop-notifications-alarms.md @@ -0,0 +1,85 @@ +# Stop notifications for individual alarms + +In this short tutorial, you'll learn how to how to stop notifications for individual alarms in Netdata's health +monitoring system. We also refer to this process as _silencing_ the alarm. + +Why silence alarms? We designed Netdata's pre-configured alarms for production systems, so they might not be +relevant if you run Netdata on your laptop or a small virtual server. If they're not helpful, they can be a distraction +to real issues with health and performance. + +Silencing individual alarms is an excellent solution for situations where you're not interested in seeing a specific +alarm but don't want to disable a [notification system](../notifications/README.md) entirely. + +## Find the alarm configuration file + +To silence an alarm, you need to know where to find its configuration file. + +Let's use the `system.cpu` chart as an example. It's the first chart you'll see on most Netdata dashboards. + +To figure out which file you need to edit, open up Netdata's dashboard and, click the **Alarms** button at the top +of the dashboard, followed by clicking on the **All** tab. + +In this example, we're looking for the `system - cpu` entity, which, when opened, looks like this: + +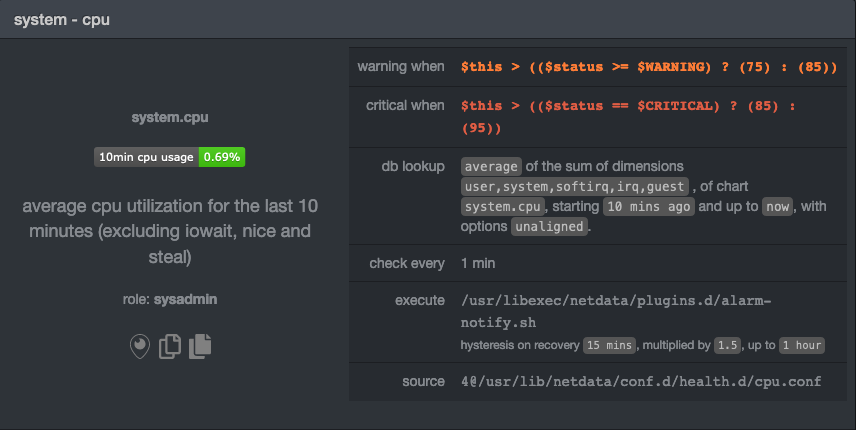 + +In the `source` row, you see that this chart is getting its configuration from +`4@/usr/lib/netdata/conf.d/health.d/cpu.conf`. The relevant part of begins at `health.d`: `health.d/cpu.conf`. That's +the file you need to edit if you want to silence this alarm. + +For more information about locating health configuration files on your system, see the [health +quickstart](../QUICKSTART.md#locate-health-configuration-files). + +## Edit the file to enable silencing + +To edit `health.d/cpu.conf`, use `edit-config` from inside of your Netdata configuration directory. + +```bash +cd /etc/netdata/ # Replace with your Netdata configuration directory, if not /etc/netdata/ +./edit-config health.d/cpu.conf +``` + +> You may need to use `sudo` or another method of elevating your privileges. + +The beginning of the file looks like this: + +```yaml +template: 10min_cpu_usage + on: system.cpu + os: linux + hosts: * + lookup: average -10m unaligned of user,system,softirq,irq,guest + units: % + every: 1m + warn: $this > (($status >= $WARNING) ? (75) : (85)) + crit: $this > (($status == $CRITICAL) ? (85) : (95)) + delay: down 15m multiplier 1.5 max 1h + info: average cpu utilization for the last 10 minutes (excluding iowait, nice and steal) + to: sysadmin +``` + +To silence this alarm, change `sysadmin` to `silent`. + +```yaml + to: silent +``` + +Use `killall -USR2 netdata` to reload your health configuration and ensure you get no more notifications about that +alarm. + +You can add `to: silence` to any alarm you'd rather not bother you with notifications. + +## What's next? + +You should now know the fundamentals behind silencing any individual alarm in Netdata. + +To learn about _all_ of Netdata's health configuration possibilities, visit the [health reference +guide](../REFERENCE.md), or check out other [tutorials on health monitoring](../README.md#tutorials). + +Or, take better control over how you get notified about alarms via the [notification +system](../notifications/README.md). + +You can also use Netdata's [Health Management API](../../web/api/health/README.md#health-management-api) to control +health checks and notifications while Netdata runs. With this API, you can disable health checks during a maintenance +window or backup process, for example. |
